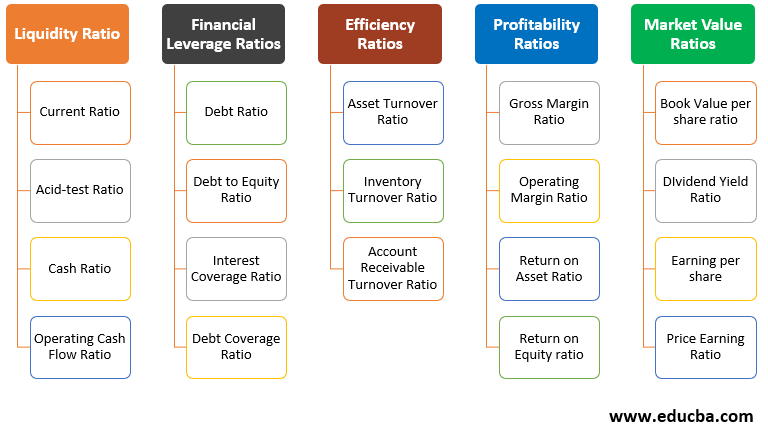
It is calculated by dividing the companys total current assets by total current liabilities. Uses and Users of Financial Ratio Analysis. As you can see there are 15 ratios beneath these categories. A debt-to-equity ratio looks at its overall debt compared to its capital supplied by investors. Leverage ratios are also referred to as debt ratios debt-to-equity ratios and interest-coverage ratios The debt ratio compares a businesss debt to its assets as a whole. Financial Analysis Type 1. Before we dive into the top 10 financial ratios lets first discuss the five major categories of ratios. Important solvency ratios include the debt to capital ratio debt ratio interest coverage ratio and equity multiplier. In other words it shows if the company uses debt or equity financing. This article throws light upon the four main types of financial ratios.
The most common types of financial analysis are. Asset turnover ratios are used to measure how efficiently a business uses its assets. O Profitability Sustainability o Operational Efficiency o Liquidity o Leverage Funding Debt Equity Grants The ratios presented below represent some of the standard ratios used in business practice and are provided as guidelines. Common financial leverage ratios are the debt to equity ratio and the debt ratio. You might also opt to examine your financial structure if you find yourself borrowing. Solvency ratios are mainly used by governments banks employees and institutional investors. An expansion project low cash reserves or a jump in expenses can prompt you to conduct such an exercise. Thus below is a comprehensive analysis of the four of the most important ratios that one should keep in mind. In general financial ratios can be broken down into four main categories. At some point most businesses require an in-depth look at their financial structure.
The current ratio is arguably one of the most essential formulas that belong to the Liquidity group. Financial Analysis Type 1. On the Basis of Material Used. Profit is both a means and end to the organization. You might also opt to examine your financial structure if you find yourself borrowing. An expansion project low cash reserves or a jump in expenses can prompt you to conduct such an exercise. Financial risk leverage analysis ratios The following section provides a summary of the five categories of financial ratios along with descriptions of how each ratio is calculated and its relevance to financial analysis. Learn more in CFIs Financial Analysis Fundamentals Course. Leverage ratios are also referred to as debt ratios debt-to-equity ratios and interest-coverage ratios The debt ratio compares a businesss debt to its assets as a whole. Financial ratios are grouped into the following categories.
Uses and Users of Financial Ratio Analysis. As you can see there are 15 ratios beneath these categories. Debt to equity refers to the amount of money and retained earnings invested in the company. The most common types of financial analysis are. There are five basic ratios that are often used to pick stocks for investment. An expansion project low cash reserves or a jump in expenses can prompt you to conduct such an exercise. It is calculated by dividing the companys total current assets by total current liabilities. The debt ratio indicates how much debt the firm is using to purchase assets. The following points highlight the four important types of financial analysis ie 1 On the Basis of Material Used and 2 On the Basis of Modus Operandi 3 On the Basis of Entities Involved and 4 On the Basis of Time Horizon or Objective of Analysis. Ratios can be divided into four major categories.
Financial Analysis Type 1. At some point most businesses require an in-depth look at their financial structure. Financial ratios are grouped into the following categories. Leverage ratios are also referred to as debt ratios debt-to-equity ratios and interest-coverage ratios The debt ratio compares a businesss debt to its assets as a whole. Price profitability liquidity debt and efficiency. Here we discuss top 5 types of ratio analysis - Profitability Solvency Liquidity Turnover and Earnings Ratios. Ratios can be divided into four major categories. There are five basic ratios that are often used to pick stocks for investment. Important solvency ratios include the debt to capital ratio debt ratio interest coverage ratio and equity multiplier. On the Basis of Material Used.